[et_pb_section fb_built=”1″ _builder_version=”4.25.2″ custom_margin=”0px||||false|false” custom_padding=”0px||||false|false” global_colors_info=”{}”][et_pb_row _builder_version=”4.25.2″ background_size=”initial” background_position=”top_left” background_repeat=”repeat” custom_margin=”0px||||false|false” custom_padding=”0px||||false|false” global_colors_info=”{}”][et_pb_column type=”4_4″ _builder_version=”4.25.2″ custom_padding=”|||” global_colors_info=”{}” custom_padding__hover=”|||”][et_pb_button button_url=”https://unimat-traffic.com/products/speed-bumps/” button_text=”Buy Speed bumps” button_alignment=”right” _builder_version=”4.25.2″ _module_preset=”default” custom_button=”on” button_text_color=”#FFFFFF” button_bg_color=”#E02B20″ button_border_color=”#E02B20″ button_icon=”||fa||900″ button_on_hover=”off” custom_margin=”-80px||||false|false” custom_css_free_form=”selector{max-width:50%;}” global_colors_info=”{}”][/et_pb_button][et_pb_text _builder_version=”4.25.2″ background_size=”initial” background_position=”top_left” background_repeat=”repeat” hover_enabled=”0″ global_colors_info=”{}” sticky_enabled=”0″]
Speed bumps and speed humps are both traffic calming devices used to slow down vehicles, but they differ in design, purpose, and application. Here’s an in-depth look at both:
Speed Bumps
Features
- Height and Width: Speed bumps are typically higher (3 to 4 inches) and narrower (1 to 3 feet wide) compared to speed humps. Their steep profile causes vehicles to slow down significantly.
- Material: Commonly made from asphalt, concrete, rubber, or plastic. Rubber speed bumps are often modular and easier to install.
- Installation Locations: Often used in parking lots, private roads, and areas where vehicle speeds need to be reduced to 5-10 mph.
Advantages
- Effectiveness: Extremely effective at reducing vehicle speed due to their sharp profile.
- Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive and easier to install than speed humps, especially rubber or plastic versions.
- Visibility: Can be enhanced with reflective tape or embedded reflectors for better visibility at night.
Disadvantages
- Comfort: Can be uncomfortable for drivers and passengers, especially at higher speeds.
- Noise: Can generate noise when vehicles pass over them, which may be a concern in residential areas.
- Emergency Vehicles: Can slow down emergency response vehicles, potentially delaying their arrival.

Speed Humps
Features
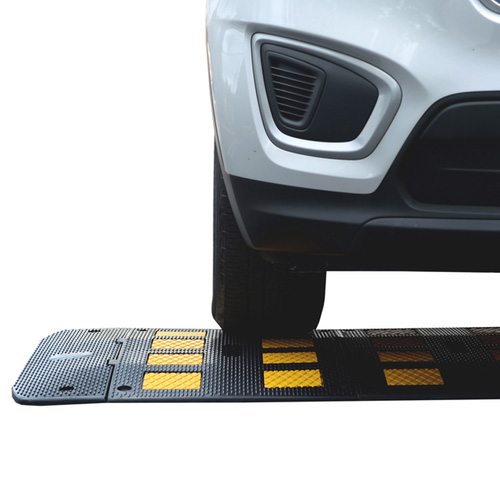
- Height and Width: Speed humps are lower (2 to 3 inches) and wider (10 to 14 feet across), with a gentler slope than speed bumps. This design slows vehicles to 10-20 mph.
- Material: Typically made from asphalt or concrete, though rubber versions are also available.
- Installation Locations: Commonly used on residential streets, school zones, and other areas where moderate speed reduction is desired without causing significant driver discomfort.
Advantages
- Comfort: Provides a smoother ride over the hump compared to speed bumps, reducing driver discomfort while still effectively slowing traffic.
- Noise: Generally quieter than speed bumps as the gradual slope causes less abrupt vehicle movements.
- Emergency Vehicles: Less impact on emergency vehicles compared to speed bumps, allowing for quicker response times.
Disadvantages
- Effectiveness: Not as effective at reducing speeds as speed bumps, especially if drivers are not cautious.
- Installation Cost: Typically more expensive and labor-intensive to install than speed bumps, especially for asphalt or concrete versions.

Comparison
Purpose
- Speed Bumps: Primarily used in areas where very low speeds are essential, such as parking lots, private driveways, and entrances to gated communities.
- Speed Humps: Used in areas where moderate speed reduction is needed without causing significant inconvenience, such as residential streets and school zones.
Impact on Traffic
- Speed Bumps: Force vehicles to slow down to 5-10 mph, causing a more abrupt speed reduction.
- Speed Humps: Encourage vehicles to slow down to 10-20 mph, promoting a steadier flow of traffic with less abrupt speed changes.
Installation and Maintenance
- Speed Bumps: Easier and cheaper to install, especially rubber and plastic versions. Require less maintenance but can be uncomfortable and noisy.
- Speed Humps: More complex and expensive to install, particularly asphalt or concrete versions. Offer a smoother ride and generate less noise.
Applications
Speed Bumps
- Parking Lots: To slow down vehicles significantly for pedestrian safety.
- Private Roads: In areas with very low speed limits.
- Driveways: To prevent speeding in residential areas.
Speed Humps
- Residential Streets: To calm traffic and enhance neighborhood safety.
- School Zones: To ensure vehicles slow down in areas with high pedestrian activity.
- Park Roads: To control speeds while maintaining a comfortable ride for drivers.
Conclusion
Both speed bumps and speed humps are effective traffic calming measures, each suited to different situations. Speed bumps are best for areas requiring significant speed reduction, while speed humps are ideal for areas needing moderate speed control without compromising driver comfort. Understanding their differences helps in choosing the appropriate solution for specific traffic management needs.
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]